What is Nasopharyngeal Cancer?
A type of throat cancer known as nasopharyngeal cancer develops in the nasopharynx, the uppermost region of the throat located in or behind the nose.
Cancer arises when cells grow uncontrollably, develop improperly, and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body.
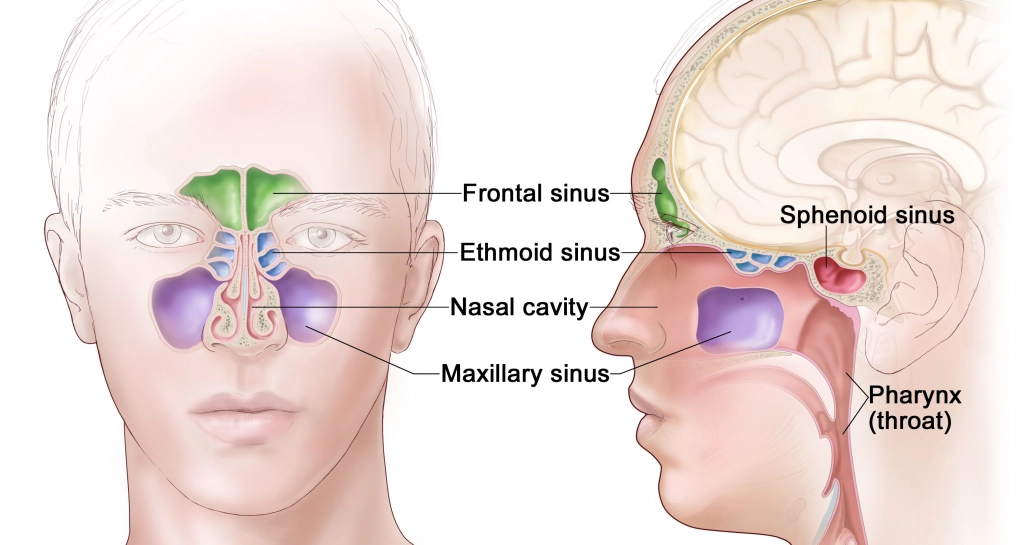
What is Nasopharynx?
The pharynx, the top part of the throat is divided into three sections:
- The nasopharynx (upper throat)
- Oropharynx (mid throat, including tonsils).
- Hypopharynx (lower throat)
Function of Nasopharynx
Breathing through the nose can pass through the larynx, the voice box, and into the lungs thanks to the nasopharynx. It also makes it possible to spit out or swallow mucus from the nose.
What leads to cancer of the Nasopharynx?
A person’s cause of cancer is frequently unknown to doctors. However, we do know what increases the risk of various malignancies.
Nasopharyngeal cancer has the following primary causes:
- Infections, including the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
- Smoking
- Most cases of nasopharyngeal cancer occur in adults 40 years of age and older.
Symptoms of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
The indications and symptoms of Nasopharyngeal Cancer depend on the location, size, and degree of the cancer’s spread throughout the body.
Typical indications and symptoms include:
- Stuffiness or blockage of the nose
- Regular bleeding from the nose
- Reduced hearing
- Clogged ears (particularly on one side only)
- A nodule in the throat
- Headaches
- Facial numbness double or blurred eyesight
These symptoms are typically not related to nasopharyngeal cancer. See your doctor right away, though, if any of these symptoms persist longer than a few weeks.
Test for Nasopharyngeal Cancergeal Cancer
It is crucial that your physician confirms the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal cancer, evaluates the cancer’s extent, and determines whether it has progressed to the body’s lymph nodes in the neck or elsewhere.
The doctor will examine your medical history, including any symptoms you may have experienced. They will request diagnostic testing, such as scans, and conduct a physical examination by feeling and looking within your throat and neck.
Nasoendoscopy – A medical treatment called a nasoendoscopy is used to look inside the throat, sinuses, nasal passages, and occasionally the upper airway and oesophagus. An endoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera attached, is used in this procedure.
Biopsy- A biopsy is a medical operation where a sample of the body’s tissue or cells is removed for microscopic inspection. Biopsies are frequently carried out in order to identify or rule out a number of medical disorders, including as cancer, infections, inflammatory illnesses, and other anomalies.
Computerised Tomography (CT) Scan
A computerised tomography (CT) scan, often called a computed axial tomography (CAT) scan, is a diagnostic imaging technique that produces finely detailed cross-sectional images of the body using computer technology and X-rays.
MRI scan, or magnetic resonance imaging
A non-invasive medical imaging method called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) creates detailed images of the body’s internal components by using radio waves and strong magnets. In contrast to ionising radiation-based procedures like CT scans and X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses the body’s inherent atomic magnetism to produce images.
PET scan, or Positron Emission Tomography
A nuclear medicine imaging method called a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan finds radioactive materials injected into the circulation and uses that information to create detailed images of the body’s internal organs and tissues.
Treatment for Nasopharyngeal cancer
Your cancer care team will discuss with you the best course of therapy, which may involve a clinical trial, after diagnosing you with Nasopharyngeal Cancer. At this time, it would be prudent to consider getting a second opinion.
The optimal course of treatment for nasopharygneal cancer depends on a number of factors, including the size and location of the malignancy.
The spread of the malignancy; personal traits (age, overall health, and previous medical history).
Remedies that are easily accessible (including clinical trial availability).
There are three different ways to treat nasopharyngeal cancer. Among them are:
Radiation therapy: High-energy waves are applied to cancer cells in order to destroy or damage them. The most popular radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal cancer is external beam radiation. This type of radiation therapy makes use of external radiation.
Surgery: Surgery may be necessary if radiation therapy is performed as a prior treatment and the cancer still returns.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to either kill or harm cancer cells. Chemotherapy is typically injected intravenously by a needle with a cannula, or tube, attached for nasopharyngeal malignancies.